Explain the type of working of proximity
Sensor
A proximity sensor detects the presence or absence of an object without direct contact. It operates using principles like infrared, ultrasonic, capacitive, or inductive sensing. Widely used in touchscreens, object detection, industrial automation, and smartphones for features like automatic screen brightness adjustment and proximity-based gestures.
Types of proximity sensor
Photoelectric Proximity Sensors: Utilize light beams for detection, including through-beam (transmitter and receiver on opposite sides) and reflective sensors (both elements on the same side).
Infrared (IR) Proximity Sensors: Detect object presence by emitting infrared light and analyzing changes in reflection patterns.
Magnetic Proximity Sensors: Identify metallic objects by detecting changes in magnetic fields caused by their presence.
Hall Effect Proximity Sensors: Use the Hall Effect to sense magnetic fields and produce an output voltage when influenced by a magnetic field.
Laser Proximity Sensors: Determine distances to objects by measuring the time it takes for laser light to reflect back.
# capacitive proximity sensor
 |
| Capacitive Proximity Sensor |
Working:
A capacitive proximity sensor is a device actuated by both conductive and non-conductive materials. A capacitor's plates are arranged by gome based on their distance separation. The capacitance measured will Therefore, proximity to the object will be detected if one of the plates of the capacitor cuts as a suritch and the other is. The metal object whose proximity is to be detected
C= £A/D
where I is permitivity is dielectric material A is the area of the plate, and d is the distance between the plates.
A capacitive proximity sensor detects the presence of an object based on changes in capacitance. It operates without physical contact, making it useful in situations where direct touch is not practical. The sensor's sensitivity is influenced by the material properties of the object and is commonly employed in touchscreens, industrial automation for object detection, and consumer electronics for touch-sensitive controls. Capacitive proximity sensors are known for their high sensitivity, quick response times, and reliability in diverse environmental conditions.
# Inductive sensor:
An inderctive sensor consists of a coil wound around a ferrous metal core detector circuit and a solid state supply voltage oscillator that operates to produce a high frequency field.
When a metallic object is placed near the field, eddy currents are induced near the field surface. These comments result in a loss of energy in the oscillator, which is tam culise, a smaller
Voltage of the oscillator The detector circuit detects a change in the amplitude and generates a signal that will result in the output device. being ON or oFF
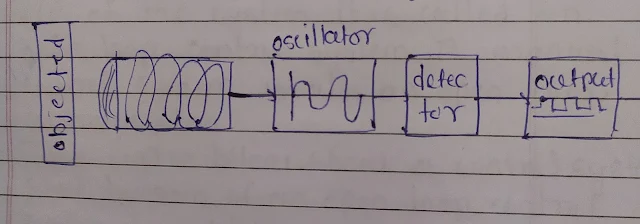 |
| Inductive sensor |
An inductive sensor detects the presence of metallic objects without direct contact. It operates based on electromagnetic induction, inducing eddy currents in a metal object within its field. The change in impedance of the sensor's coil is detected, signaling the presence of a metallic object.
Inductive sensors are commonly used in industrial automation for metal detection, object sensing in machinery, and position sensing in manufacturing processes. They are appreciated for their reliability, durability, and suitability for harsh conditions, being resistant to dirt, dust, and moisture.
Ultrasonic proximity sensor:
To find things and gauge their distance from them, an ultrasonic proximity sensor sends out ultrasonic waves, which are usually inaudible sound waves. It sends and receives these waves using a transducer, measuring distance by measuring the time it takes for the sound waves to travel back and forth.. Commonly found in robotics, industrial automation, and vehicle parking systems, ultrasonic sensors offer non-contact detection and work effectively in various environments, though they may face challenges in noisy or turbulent conditions. They can operate in proximity mode to detect objects or in distance measurement mode for precise distance calculations.
Photoelectric Proximity Sensors:
A photoelectric proximity sensor operates by emitting light, usually infrared, and detecting changes in the transmitted light when an object enters its field. It consists of an emitter producing the light beam and a receiver sensing changes when the beam is interrupted by an object. There are different modes: through-beam, reflective, and diffuse-reflective. These sensors are used in applications like object detection on conveyor belts, liquid level control, and automated machinery. Offering non-contact sensing, they can detect a variety of materials, though factors like ambient light and material properties can impact performance.
Infrared (IR) Proximity Sensors:
IR proximity sensors use infrared light to detect the presence or absence of objects and measure distance. They consist of an emitter sending out IR light and a receiver detecting the reflected light. The distance is determined by measuring the time it takes for the light to reflect back. Common types include reflective, break-beam (through-beam), and diffuse reflective sensors. IR sensors are employed in mobile devices, motion detectors, robotics, and security systems due to their non-contact sensing and effectiveness in various lighting conditions. However, their accuracy may be affected by factors like ambient light and object reflectivity.
Application of the proximity sensor:
-
Automotive: Applied in parking assistance, obstacle detection, and keyless entry systems.
-
Industrial automation is crucial for object detection in conveyor systems, assembly lines, and robotics, ensuring precise control.
-
Touchless Switches: Implemented in doors, elevators, and sanitary fixtures for touchless operation in public spaces.
-
Human Machine Interface (HMI): integrated into touchscreens and interactive displays, offering touchless user interaction.
-
Security Systems: Contribute to detecting unauthorized access or movement in restricted areas.
-
Vending machines are used to detect the presence of an object near the dispensing area for safe operation.

